Fighting Type 2 Diabetes in India
Type 2 diabetes is a growing health crisis in India. As one of the countries with the highest prevalence of diabetes globally, India faces significant challenges associated with this chronic disease. According to the World Health Organization, the number of individuals living with diabetes in India is expected to rise to 134 million by 2045.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
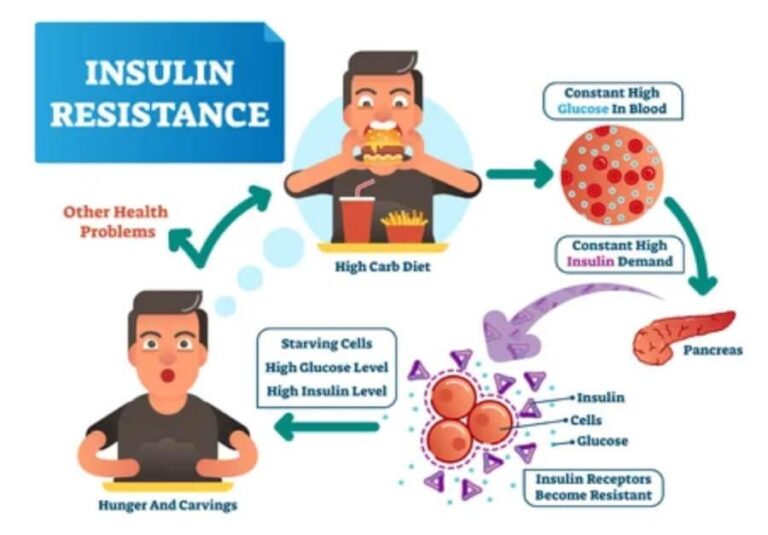
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin. This metabolic disorder is often linked to obesity, inactivity, and unhealthy dietary habits. In India, the rapid urbanization and adoption of Western lifestyles have contributed significantly to the rising rates of this disease.
Risk Factors in India
Several risk factors contribute to the high prevalence of Type 2 diabetes in India. Genetics, dietary patterns, physical inactivity, and socioeconomic factors all play a critical role. Particularly, the shift towards high-calorie, processed foods has heightened the risk of obesity, which is a major precursor to diabetes.
Government Initiatives
The Indian government has launched various initiatives to combat Type 2 diabetes. Campaigns focused on raising awareness and promoting healthy lifestyles are essential in addressing this public health challenge. One such initiative includes the National Program for Prevention and Control of Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS).
Community Action and Support
Community-based interventions can significantly impact diabetes management and prevention. Local organizations are increasingly focusing on education and support programs that empower individuals to make healthier choices. For effective strategies and ongoing support, initiatives like those described by The Borgen Project are invaluable in the fight against Type 2 diabetes in India. Learn more about the ongoing efforts to tackle this pressing issue.
Conclusion
Addressing Type 2 diabetes in India requires a multifaceted approach. Governments, communities, and individuals must work together to implement prevention strategies and promote healthy lifestyles. With concerted efforts, there is hope for reducing the burden of diabetes and improving the quality of life for millions in India.