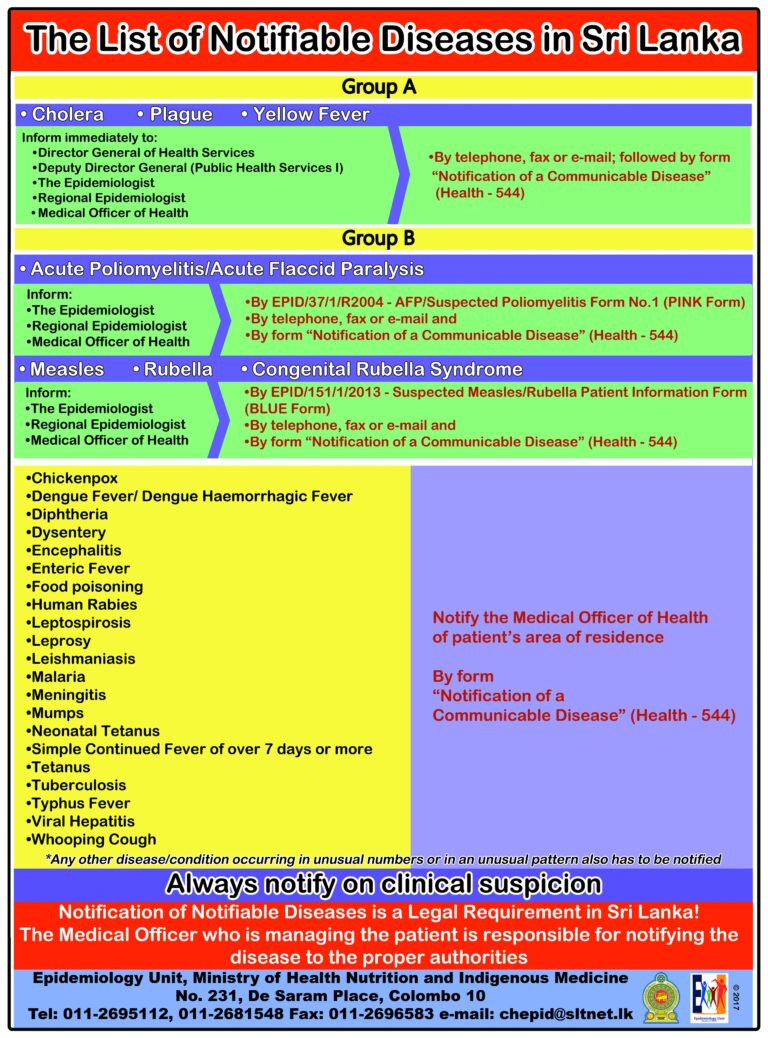
Introduction
Diseases pose a significant threat to public health around the world, and Sri Lanka is no exception. The island nation has been grappling with various diseases that significantly affect its population. Understanding these health challenges is crucial for implementing effective interventions.
Common Communicable Diseases
Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is one of the most prevalent vector-borne diseases in Sri Lanka. The disease is transmitted by the Aedes mosquito, and outbreaks typically occur during the monsoon season. Prevention efforts focus on mosquito control and public awareness.
Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is another infectious disease that affects many Sri Lankans, particularly during the rainy season. The disease is caused by a bacterial infection from water contaminated with animal urine. Public health campaigns aim to educate the population on minimizing risk factors.
Non-Communicable Diseases
Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a leading cause of mortality in Sri Lanka. Rapid urbanization and lifestyle changes have contributed to rising risk factors such as obesity and sedentary behavior. Efforts to reduce CVDs include promoting better nutrition and increased physical activity.
Diabetes
Diabetes is becoming increasingly prevalent among the Sri Lankan population, especially in urban areas. Factors such as unhealthy diets and lack of exercise are contributing to this alarming trend. Community health programs are essential to improve awareness and management of diabetes.
Challenges in Health Infrastructure
The health infrastructure in Sri Lanka faces numerous challenges, including resource limitations and uneven access to healthcare. Rural areas often lack adequate medical facilities, making it difficult to treat prevalent diseases effectively. Investment in health services and technology is critical for improvement.
Conclusion
diseases impacting Sri Lanka range from communicable to non-communicable illnesses. Addressing these health issues requires a multi-faceted approach involving policymakers, healthcare providers, and communities. For more information on how diseases affect the country, visit this resource.